Image Source: iStockPhoto
The quest to look gorgeous can be frustrating because of different kinds of skin lesions. And to most persons with skin moles, the easiest approach to a removal of the abnormal skin pigment is highly welcomed. Moles (also called melanocytic nevus) are pigments on the skin caused by the clustering of melanocyte cells. It may occur during embryologic development or result from environmental factors subjected to the skin. Research conducted by JAMA Network in 2016 revealed that a good percentage of skin moles in people have contributed in one way or the other to the growth of this skin disorder. Others were referred to be genetically induced and from hormonal imbalances.Moles may be visible as a dark or brown spot. It usually becomes darker when exposed to the sun especially before the patient exceeds teen years.
Types of Moles
Melanocytic nevus has been classified based on their site of occurrence, size, origin and its level of risk that can lead to cancer. These types of moles may be diagnosed by a dermatologist using the ABCDE examination guide. The guide simply depicts the melanocytic nevus to be regular or irregular shaped, scalloped or notched borders, even or uneven coloured, different size in diameter and the growth of moles over time respectively. Below are the most famous forms of moles.
Congenital nevus
This form of moles is usually caused by the mutation of embryonic cells. Hence, it comes in the form of birthmarks when a child is born. Congenital nevus moles occur rarely; one child in hundred births and usually occur at the neck or head region of the infant. It varies in sizes. The mole size and number demonstrates the patient’s risk of developing melanoma (skin cancer). More moles increase the risk.Congenital nevus has its origin in the genes responsible for coding the KRAS and NRAS proteins.And no prevention measure has been clinically established for now.
Mongolian spot
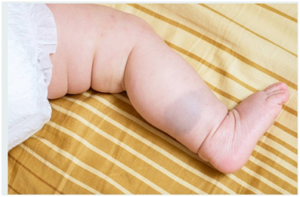
A Mongolian spot is also known as congenital dermal melanocytosis. This is because its origin is in the embryologic development and it comes also in the form of a birthmark. Mongolian spot appears after about three years of the child’s birth or before puberty. This type of mole is completely flat and usually irregular in shape. The color is usually blue or with a mixture of brown or deep brown. A Mongolian spot is caused by the entrapment of melanocyte cells in the dermis and has no chance of developing into melanoma.
Dysplastic Nevus
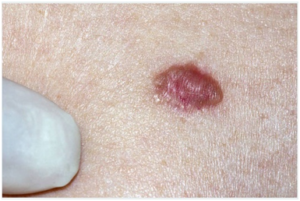
A dysplastic nevus occurs differently from common moles because they grow over time. This type of mole can also be referred to as atypical moles. It usually begins as a flat pigment but gradually grow larger than common moles. This skin lesion may be irregular in shape, it will be colored and rises incredibly above the skin surface. The mole site is usually on the trunk in men and within the calves in women, all though it may develop in any other region of the skin. A dysplastic nevus is the most harmful form of moles because it easily develops into skin cancer (melanoma). Genetic disorders have been recognized as the main cause for the formation of the mole. However, environmental conditions related to skin exposure to sun and tanning are acknowledged as more contributing factors. Preventions of dysplastic nevus include the use of sunscreen although the year, avoidance of tanning and regularly covering up the body.
Blue nevus
This mole is one of the harmless skin pigments. It’s usually very deep into the skin and appears as a gray-blue patch or blue-black nodule. Blue nevus is classified as patch blue nevus, malignant blue nevus, nevus ceruleous, deep penetrating nevus, epithelioid blue nevus, cellular blue nevus and amelanotic blue nevus. Causes of this mole are closely related to dysplastic nevus; this makes the two types to mimic each other sometimes. Blue nevus prevention is similar to dysplastic nevus.
Spitz nevus
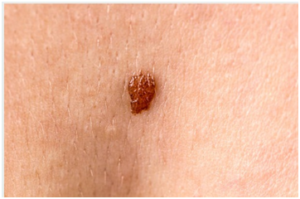
Spitz nevus is another lethal form of moles also referred to as benign juvenile melanoma, though the juvenile has been dropped recently to stop confusion. This is mostly because Spitz nevus does not occur in children. It’s a mole associated with adults, mostly from ages above 40 years. Spitz nevus affects the epidermis and dermis. The mole’s origin is yet to be discovered, but many research ties the cause with sunburn. Prevention is to avoid skin exposure to UV light and to avoid tanning.
Treatment of Moles
Skin biopsy is the most prominent treatment used by pathologists. And proper care is required for removing moles from the beginning to avoid its regeneration. Most importantly, the original mole’s location and size contribute to the most suitable method to be used. Recently, Laser, surgery or electrocautery has been very effective in the removal of moles.